Grand Junction Canal on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
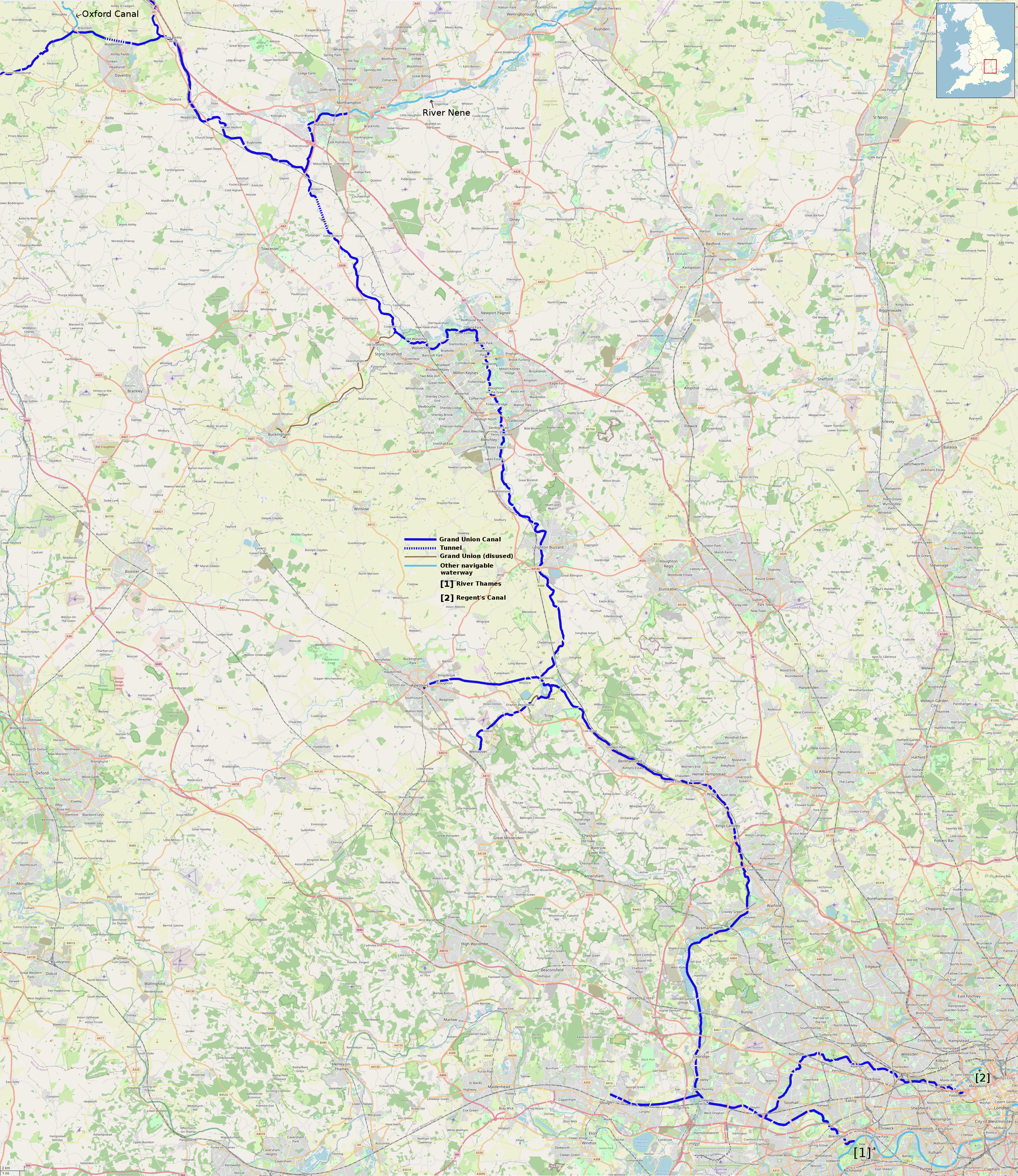
The Grand Junction Canal is a
 At the north end, there were problems with the construction of Blisworth Tunnel: quicksand was encountered, and errors made in alignment which meant that the tunnel had a pronounced wiggle. With the opening of
At the north end, there were problems with the construction of Blisworth Tunnel: quicksand was encountered, and errors made in alignment which meant that the tunnel had a pronounced wiggle. With the opening of Northamptonshire's First Railway, The Blisworth Hill Railway 1800–1805
/ref> James Barnes proposed that work begin again on the tunnel on a new line.
 The 1794 act authorised three further branches, to
The 1794 act authorised three further branches, to
 An inclined plane was opened at
An inclined plane was opened at
Internet Archive
*''The Mechanics' Magazine, Museum, Register, Journal and Gazette''. (1834) Letter: "Improvement in the Locks of the Grand Junction Canal Company"
Google Books
*Hiscock, Fabian, (2019) ''
canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flow un ...
in England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
from Braunston
Braunston is a village and civil parish in West Northamptonshire, England, next to the border with Warwickshire. At the 2011 Census, the parish had a population of 1,759. Braunston is situated just off the A45 main road and lies between the to ...
in Northamptonshire
Northamptonshire (; abbreviated Northants.) is a county in the East Midlands of England. In 2015, it had a population of 723,000. The county is administered by
two unitary authorities: North Northamptonshire and West Northamptonshire. It is ...
to the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, se ...
at Brentford
Brentford is a suburban town in West London, England and part of the London Borough of Hounslow. It lies at the confluence of the River Brent and the Thames, west of Charing Cross.
Its economy has diverse company headquarters buildings whi ...
, with a number of branches. The mainline was built between 1793 and 1805, to improve the route from the Midlands
The Midlands (also referred to as Central England) are a part of England that broadly correspond to the Kingdom of Mercia of the Early Middle Ages, bordered by Wales, Northern England and Southern England. The Midlands were important in the Ind ...
to London, by-passing the upper reaches of the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, se ...
near Oxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
, thus shortening the journey.
In 1927 the canal was bought by the Regent's Canal
Regent's Canal is a canal across an area just north of central London, England. It provides a link from the Paddington Arm of the Grand Union Canal, north-west of Paddington Basin in the west, to the Limehouse Basin and the River Thames in eas ...
Company and, since 1 January 1929, has formed the southern half of the Grand Union Main Line from London to Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the West ...
. The canal is now much used by leisure traffic.
Isambard Kingdom Brunel
Isambard Kingdom Brunel (; 9 April 1806 – 15 September 1859) was a British civil engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history," "one of the 19th-century engineering giants," and "one ...
's last major undertaking was the compact Three Bridges, London, on the canal. Work began in 1856, and was completed in 1859. The three bridges are an overlapping arrangement allowing the routes of the Grand Junction Canal, Great Western and Brentford Railway, and Windmill Lane to cross.
History
Need
By 1790, an extensive network of canals was in place, or under construction, in the Midlands. However, the only route to London was via theOxford Canal
The Oxford Canal is a narrowboat canal in central England linking the City of Oxford with the Coventry Canal at Hawkesbury (just north of Coventry and south of Bedworth) via Banbury and Rugby. Completed in 1790, it connects to the River Thame ...
to the River Thames at Oxford, and then down the river to the capital. The river, particularly the upper reaches, was in a poor condition for navigation compared with the modern canals. The river suffered from shallow sections and shortage of water leading to delays at locks, and there were frequent conflicts with mill owners over water supplies.
In 1791–92, two surveys of a route from Brentford on the Thames to Braunston on the Oxford Canal were carried out, first by James Barnes and then by William Jessop
William Jessop (23 January 1745 – 18 November 1814) was an English civil engineer, best known for his work on canals, harbours and early railways in the late 18th and early 19th centuries.
Early life
Jessop was born in Devonport, Devon, the ...
. There were other proposals for an alternative direct route to London, and two bills were put to Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
, but it was the Bill for the Grand Junction Canal which was passed on 30 April 1793.
Construction
TheAct of Parliament
Acts of Parliament, sometimes referred to as primary legislation, are texts of law passed by the Legislature, legislative body of a jurisdiction (often a parliament or council). In most countries with a parliamentary system of government, acts of ...
authorised the company to raise up to £600,000 to fund construction of the main line from where the eastern branch of the River Brent
The River Brent is a river in west and northwest London, England, and a tributary of the River Thames. in length, it rises in the Borough of Barnet and flows in a generally south-west direction before joining the Tideway stretch of the Thame ...
enters the Thames adjoining Syon Park
Syon Park is the garden of Syon House, the London home of the Duke of Northumberland in Isleworth in the London Borough of Hounslow. It was landscaped by Capability Brown in the 18th century, and it is Grade I listed by English Heritage under ...
in the parish of Brentford, to the Oxford Canal at Braunston. It also authorised branches to Daventry
Daventry ( , historically ) is a market town and civil parish in the West Northamptonshire unitary authority in Northamptonshire, England, close to the border with Warwickshire. At the 2021 Census Daventry had a population of 28,123, making ...
, the River Nene
The River Nene ( or : see below) is a river in the east of England that rises from three sources in Northamptonshire.OS Explorer Map sheet 223, Northampton & Market Harborough, Brixworth & Pitsford Water. The river is about long, about of w ...
at Northampton
Northampton () is a market town and civil parish in the East Midlands of England, on the River Nene, north-west of London and south-east of Birmingham. The county town of Northamptonshire, Northampton is one of the largest towns in England; ...
, to the turnpike
Turnpike often refers to:
* A type of gate, another word for a turnstile
* In the United States, a toll road
Turnpike may also refer to:
Roads United Kingdom
* A turnpike road, a principal road maintained by a turnpike trust, a body with powers ...
road (now the A5) at Old Stratford
Old Stratford is a village and wider civil parish in the south of the English county of Northamptonshire. The population of the civil parish (including Passenham) at the 2011 Census was 1,935. The 'Stratford' part of the village name is Anglo-Sax ...
, and to Watford
Watford () is a town and borough in Hertfordshire, England, 15 miles northwest of Central London, on the River Colne.
Initially a small market town, the Grand Junction Canal encouraged the construction of paper-making mills, print works, a ...
: those to Daventry and Watford were not built.
William Jessop was appointed to take charge of construction which started almost immediately from both ends. On 3 June 1793 an engineer, James Barnes, was appointed at the rate of two guineas
The guinea (; commonly abbreviated gn., or gns. in plural) was a coin, minted in United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, Great Britain between 1663 and 1814, that contained approximately one-quarter of an ounce of gold. The name came from t ...
(£2 2 s) per day plus half a guinea (10s 6 d) expenses.
 At the north end, there were problems with the construction of Blisworth Tunnel: quicksand was encountered, and errors made in alignment which meant that the tunnel had a pronounced wiggle. With the opening of
At the north end, there were problems with the construction of Blisworth Tunnel: quicksand was encountered, and errors made in alignment which meant that the tunnel had a pronounced wiggle. With the opening of Braunston Tunnel
Braunston Tunnel is on the Grand Union Canal about 830 yds (760 m) east of Braunston, Northamptonshire, England top lock. It is in the northern outskirts of Daventry, about 2 km east of the village of Braunston.
Braunston Tunnel is 2, ...
, the line was open from the Oxford Canal through to Weedon Bec
Weedon Bec, usually just Weedon, is a village and parish in West Northamptonshire, England. It is close to the source of the River Nene. The population of the civil parish at the 2011 census was 2,706.
Geography
Weedon is around southeas ...
in June 1796. However, Blisworth Tunnel continued to cause problems, collapsing in January 1796. The canal was opened from Braunston to Blisworth in 1797. The canal from the Thames reached Two Waters near Hemel Hempstead
Hemel Hempstead () is a town in the Dacorum district in Hertfordshire, England, northwest of London, which is part of the Greater London Urban Area. The population at the 2011 census was 97,500.
Developed after the Second World War as a ne ...
in 1798, Bulbourne at the north end of the Tring
Tring is a market town and civil parish in the Borough of Dacorum, Hertfordshire, England. It is situated in a gap passing through the Chiltern Hills, classed as an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, from Central London. Tring is linked to ...
summit in 1799, and Stoke Bruerne
Stoke Bruerne is a small village and civil parishes in England, civil parish in West Northamptonshire, England about north of Milton Keynes and south of Northampton.
The civil parish population at the 2011 Census was 373.
History
Stoke Brue ...
at the south end of Blisworth Tunnel the following year.
Thus, with the exception of Blisworth Tunnel, the main line was fully open in 1800. To allow goods to cross the gap, a road was built in 1800 over the top of Blisworth hill and, later, upon the recommendation of committee member Joseph Wilkes
Joseph Wilkes (1733–1805) was an 18th-century English industrialist and agricultural improver born in the village of Overseal in Derbyshire but more commonly associated with the village of Measham in Leicestershire.
From a farming family, Wil ...
, Benjamin Outram
Benjamin Outram (1 April 1764 – 22 May 1805) was an English civil engineer, surveyor and industrialist. He was a pioneer in the building of canals and tramways.
Life
Born at Alfreton in Derbyshire, he began his career assisting his father ...
was contracted to build a tramway over the hill./ref> James Barnes proposed that work begin again on the tunnel on a new line.
Robert Whitworth
Robert Whitworth (1734 – 30 March 1799) was an English land surveyor and engineer, who learnt his trade under John Smeaton and James Brindley, and went on to become one of the leading canal engineers of his generation.
Biography
Whitworth was ...
and John Rennie were called in for advice, and supported this proposal. However, construction on the new line did not start until June 1802, and was not completed until March 1805.
Initially, nine locks were used in a temporary arrangement to lower and raise the canal for the crossing of the River Great Ouse
The River Great Ouse () is a river in England, the longest of several British rivers called "Ouse". From Syresham in Northamptonshire, the Great Ouse flows through Buckinghamshire, Bedfordshire, Cambridgeshire and Norfolk to drain into the Wa ...
at Wolverton
Wolverton is a constituent town of Milton Keynes, England. It is located at the northern edge of Milton Keynes, beside the West Coast Main Line, the Grand Union Canal and the river Great Ouse. It is the administrative seat of Wolverton and Gre ...
at the river's water level. In 1799, William Jessop designed a three-arch masonry aqueduct and embankment to cross the river and replace the locks. This collapsed in 1808, and a wooden trough was used as a temporary replacement. It was decided to build an iron aqueduct, with Benjamin Bevan
Benjamin Bevan (26 December 1773 — 2 July 1833) was a British civil engineer, noted for his proof of the equivalence of the elastic moduli of ice and water. He was a principal engineer on the Grand Junction Canal.
Bevan was born on Boxi ...
as engineer. The foundation stone for the replacement aqueduct was laid on 9 September 1809, and it was opened on 22 January 1811.
The Grand Junction Canal had reduced the distance to London from the Midlands by —via Oxford and the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, se ...
—and made the journey reliable. As a result, it thrived: in 1810 it carried 343,560 tons of goods through London, with roughly equal amounts into and out of the capital.
The branches
The Grand Junction's original act in 1793 authorised branches to Daventry, theRiver Nene
The River Nene ( or : see below) is a river in the east of England that rises from three sources in Northamptonshire.OS Explorer Map sheet 223, Northampton & Market Harborough, Brixworth & Pitsford Water. The river is about long, about of w ...
at Northampton, to the turnpike
Turnpike often refers to:
* A type of gate, another word for a turnstile
* In the United States, a toll road
Turnpike may also refer to:
Roads United Kingdom
* A turnpike road, a principal road maintained by a turnpike trust, a body with powers ...
road at Old Stratford (north-west of the modern Milton Keynes
Milton Keynes ( ) is a city and the largest settlement in Buckinghamshire, England, about north-west of London. At the 2021 Census, the population of its urban area was over . The River Great Ouse forms its northern boundary; a tributary ...
), and to Watford
Watford () is a town and borough in Hertfordshire, England, 15 miles northwest of Central London, on the River Colne.
Initially a small market town, the Grand Junction Canal encouraged the construction of paper-making mills, print works, a ...
in Hertfordshire
Hertfordshire ( or ; often abbreviated Herts) is one of the home counties in southern England. It borders Bedfordshire and Cambridgeshire to the north, Essex to the east, Greater London to the south, and Buckinghamshire to the west. For govern ...
: those to Daventry and Watford were not built. The branch to Old Stratford was amended before it was built (see below). The branch to Northampton was delayed as the plans of the Leicestershire and Northamptonshire Union Canal
The Leicestershire and Northamptonshire Union Canal is a canal in England that is now part of the Grand Union Canal.
It was authorised by an Act of Parliament in 1793 to connect Leicester to the Nene near Northampton and to join the projected li ...
to reach Northampton and thus join with the Grand Junction came to nothing. The link to Northampton was made by a tramroad transferred from Blisworth Tunnel, with the canal from Gayton being opened in 1815. The link to Leicester
Leicester ( ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, city, Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority and the county town of Leicestershire in the East Midlands of England. It is the largest settlement in the East Midlands.
The city l ...
was eventually achieved by the opening of the Grand Union Canal
The Grand Union Canal in England is part of the British canal system. It is the principal navigable waterway between London and the Midlands. Starting in London, one arm runs to Leicester and another ends in Birmingham, with the latter st ...
, which took a more direct route from Foxton in Leicestershire
Leicestershire ( ; postal abbreviation Leics.) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in the East Midlands, England. The county borders Nottinghamshire to the north, Lincolnshire to the north-east, Rutland to the east, Northamptonshire t ...
to the Grand Junction at Norton Junction.
 The 1794 act authorised three further branches, to
The 1794 act authorised three further branches, to Aylesbury
Aylesbury ( ) is the county town of Buckinghamshire, South East England. It is home to the Roald Dahl Children's Gallery, David Tugwell`s house on Watermead and the Waterside Theatre. It is in central Buckinghamshire, midway between High Wy ...
, Buckingham
Buckingham ( ) is a market town in north Buckinghamshire, England, close to the borders of Northamptonshire and Oxfordshire, which had a population of 12,890 at the 2011 Census. The town lies approximately west of Central Milton Keynes, sou ...
, and Wendover
Wendover is a market town and civil parish at the foot of the Chiltern Hills in Buckinghamshire, England. It is situated at the point where the main road across the Chilterns between London and Aylesbury intersects with the once important road a ...
. The navigable feeder from Wendover to the summit level at Tring was opened in 1799, while the Buckingham branch
Buckingham Branch Railroad is a Class III short-line railroad operating over 275 miles (443 km) of historic and strategic trackage in Central Virginia. Sharing overhead traffic with CSX and Amtrak, the company's headquarters are in Dillw ...
, an extension of the original proposal for a link to the main road at Old Stratford, was opened in 1801: both eventually fell into disuse, though the Wendover Arm is undergoing active restoration, and part of it is again navigable. The Aylesbury arm was envisaged to become a through route to the Thames and thus to the Wilts and Berks Canal
The Wilts & Berks Canal is a canal in the historic counties of Wiltshire and Berkshire, England, linking the Kennet and Avon Canal at Semington near Melksham, to the River Thames at Abingdon. The North Wilts Canal merged with it to become a b ...
and the Kennet and Avon Canal
The Kennet and Avon Canal is a waterway in southern England with an overall length of , made up of two lengths of navigable river linked by a canal. The name is used to refer to the entire length of the navigation rather than solely to the cent ...
, but the 6-mile (10-kilometre) branch into the town, opened in 1815, was never extended.
The act of April 1795 authorised a branch to Paddington
Paddington is an area within the City of Westminster, in Central London. First a medieval parish then a metropolitan borough, it was integrated with Westminster and Greater London in 1965. Three important landmarks of the district are Paddi ...
from Bull's Bridge near Hayes: this was completed in 1801 and, with its large basin at Paddington and many wharfs along its length, it became an important trade route, even more so with the subsequent opening of the Regent's Canal
Regent's Canal is a canal across an area just north of central London, England. It provides a link from the Paddington Arm of the Grand Union Canal, north-west of Paddington Basin in the west, to the Limehouse Basin and the River Thames in eas ...
. This branch also acted as a source of water from the River Brent.
The act of June 1795 authorised a branch to St Albans: this was not built.
The last branch to be authorised and built was the route to Slough
Slough () is a town and unparished area in the unitary authority of the same name in Berkshire, England, bordering west London. It lies in the Thames Valley, west of central London and north-east of Reading, at the intersection of the M4 ...
, opened in 1882.
Acts of Parliament
* 33 Geo. III c. 80, received Royal Assent on 30 April 1793 ::An Act for making and maintaining a navigable Canal from the Oxford Canal Navigation at Braunston, in the county of Northampton, to join the River Thames at or near Brentford, in the county of Middlesex; and also certain collateral Cuts from the said intended Canal. * 34 Geo. III c. 24, received Royal Assent on 28 March 1794 ::An Act for making certain navigable Cuts from the towns of Buckingham, Aylesbury, and Wendover, in the county of Buckingham, to communicate with the Grand Junction Navigation authorized to be made by an Act of the last Session of Parliament, and for amending the said Act. * 35 Geo. III c. 8, received Royal Assent on 5 March 1795 ::An Act for authorizing the Company of the Grand Junction Canal to vary the Course of a certain Part of the said Canal, in the county of Hertford, so as to render the Navigation thereof more safe and convenient, and for making some other Amendments and Alterations in an Act made in the Thirty-third Year of the Reign of his present Majesty, for making the said Canal. * 35 Geo. III c. 43, received Royal Assent on 28 April 1795 ::An Act for making a navigable Cut from the Grand Junction Canal, in the precinct of Norwood, in the county of Middlesex, to Paddington, in the said county * 35 Geo. III c. 85, received Royal Assent on 2 June 1795 ::An Act for making and extending a navigable Cut from the town of Watford, in the county of Hertford, to the town of St. Alban, in the same county, * 36 Geo. III c. 25, received Royal Assent on 24 December 1795 ::An Act to enable the Company of Proprietors of the Grand Junction Canal to finish and complete the same, and the several Cuts and other Works authorized to be made and done by them, by virtue of several Acts of Parliament * 38 Geo. III c. 33, received Royal Assent on 26 May 1798 ::An Act for confirming and carrying into Execution certain Articles of Agreement made and entered into between Beilby, Lord Bishop of London, Thomas Wood, Esq. Sir John Frederick, Bart. and Arthur Stanhope, Esq. Sir John Morshead, Bart. and Dame Elizabeth his wife, and Robert Thistlethwaite, Esq. and Selina his wife, and the Company of Proprietors of the Grand Junction Canal; and for other Purposes therein-mentioned * 41 Geo. III c. 71, received Royal Assent on 20 June 1801 ::An Act for enabling the Company of Proprietors of the Grand Junction Canal more effectually to provide for the Discharge of their Debts, and to complete the whole of the Works to be executed by them, in pursuance of the several Acts of the Thirty-third, Thirty-fourth, Thirty-fifth, Thirty-sixth, and Thirty-eighth Years of the Reign of his present Majesty; and for altering and enlarging the Powers and Provisions of the said Acts * 43 Geo. III c. 8, received Royal Assent on 24 March 1803 ::An Act for empowering the Company of Proprietors of the Grand Junction Canal, to raise a further Sum of Money to enable them to complete the Works authorized to be executed, in pursuance of the several Acts passed in the Thirty-third, Thirty-fourth, Thirty-fifth, Thirty-sixth, Thirty-eighth, and Forty-first Years of the Reign of his present Majesty; and for amending, altering, and enlarging the Powers and Provisions of the said Acts * 45 Geo. III c. 68, received Royal Assent on 27 June 1805 ::An Act for altering, amending, and enlarging the Powers of certain Acts for making and maintaining the Grand Junction Canal * 52 Geo. III c. 140, received Royal Assent on 9 June 1812 ::An Act to explain, amend, and enlarge the Powers of certain Acts passed for making and maintaining the Grand Junction Canal * 58 Geo. III c. 16, received Royal Assent on 17 March 1818 ::An Act to enable the Grand Junction Canal Company to vary the Line of Part of their Canal in the county of Hertford, and for altering and enlarging the Powers of several Acts relating to the said Canal. * 59 Geo. III c. 111, received Royal Assent on 22 June 1819 ::An Act to vary and alter certain Acts of his present Majesty, relating to the Grand Junction Canal, the Grand Junction Water Works, and the Regent's Canal, in order to effect an Exchange of Water, for the better Supply of the Regent's Canal Navigation and Grand Junction Water Works. This list is incomplete. Among those missing are the act authorising construction of the Slough Arm, and acts in 1928 authorising the formation of theGrand Union Canal
The Grand Union Canal in England is part of the British canal system. It is the principal navigable waterway between London and the Midlands. Starting in London, one arm runs to Leicester and another ends in Birmingham, with the latter st ...
.
Further development
A clause under their acts allowed the Grand Junction Canal to supply drinking water. Accordingly, theGrand Junction Waterworks Company
The Grand Junction Waterworks Company was a utility company supplying water to parts of west London in England. The company was formed as an offshoot of the Grand Junction Canal Company in 1811 and became part of the publicly owned Metropoli ...
was established in 1811, initially taking water from the River Colne, the River Brent
The River Brent is a river in west and northwest London, England, and a tributary of the River Thames. in length, it rises in the Borough of Barnet and flows in a generally south-west direction before joining the Tideway stretch of the Thame ...
and a reservoir in North West Middlesex now known as Ruislip Lido
Ruislip ( ) is an area in the London Borough of Hillingdon in West London, and in the historic county of Middlesex. Ruislip lies west-north-west of Charing Cross, London.
The manor of Ruislip appears in the Domesday Book, and some of the ear ...
. These waters proved unsatisfactory and the company transferred its inlets to the River Thames.
The importance of trade between London and the Midlands meant that railway competition was an early threat to this canal compared with others in the country. John Rennie undertook a survey in 1824 for a London to Birmingham railway.
There were also ambitious proposals for new canals. In 1827 there was a proposal for a London and Birmingham Junction Canal from the Stratford-upon-Avon Canal
The Stratford-upon-Avon Canal is a canal in the south Midlands of England. The canal, which was built between 1793 and 1816, runs for in total, and consists of two sections. The dividing line is at Kingswood Junction, which gives access to the ...
to Braunston. In 1832, William Cubitt
Sir William Cubitt FRS (bapt. 9 October 1785 – 13 October 1861) was an eminent English civil engineer and millwright. Born in Norfolk, England, he was employed in many of the great engineering undertakings of his time. He invented a type of ...
proposed a Central Union Canal from the Worcester and Birmingham Canal
The Worcester and Birmingham Canal is a canal linking Birmingham and Worcester in England. It starts in Worcester, as an 'offshoot' of the River Severn (just after the river lock) and ends in Gas Street Basin in Birmingham. It is long.
There ar ...
near Worcester Bar via Solihull
Solihull (, or ) is a market town and the administrative centre of the wider Metropolitan Borough of Solihull in West Midlands County, England. The town had a population of 126,577 at the 2021 Census. Solihull is situated on the River Blythe i ...
to the Oxford at Ansty, while in 1833 there were proposals for a London and Birmingham Canal, from Stratford direct to the Regent's Canal, which would bypass the Grand Junction Canal entirely. This, together with the railway threats, spurred the Grand Junction into making improvements.
The London and Birmingham Railway
The London and Birmingham Railway (L&BR) was a railway company in the United Kingdom, in operation from 1833 to 1846, when it became part of the London and North Western Railway (L&NWR).
The railway line which the company opened in 1838, betw ...
was completed in 1838 and, with the exception of the Oxford Canal, the canals on the route from London to Birmingham co-operated to reduce tolls to compete with the railway. As a result, there was an increase in traffic, but income was significantly reduced.
To cope with the traffic volumes, the locks at Stoke Bruerne
Stoke Bruerne is a small village and civil parishes in England, civil parish in West Northamptonshire, England about north of Milton Keynes and south of Northampton.
The civil parish population at the 2011 Census was 373.
History
Stoke Brue ...
were duplicated in 1835, and new larger reservoirs built at Tring to ease a serious water shortage. In 1848 the Grand Junction entered the carrying trade, pitting its boats directly against the railway competition. From 1864, steam narrow boats
A narrowboat is a particular type of canal boat, built to fit the narrow locks of the United Kingdom. The UK's canal system provided a nationwide transport network during the Industrial Revolution, but with the advent of the railways, commer ...
were acquired, working with a butty, and these penetrated as far as the Erewash Canal
The Erewash Canal is a broad canal in Derbyshire, England. It runs just under and has 14 canal lock, locks. The first lock at Langley Mill, Langley Bridge is part of the Cromford Canal.
Origins
The canal obtained its act of parliament in ...
. Carrying was given up in 1876 because it did not pay.
By 1871 the tunnels at Braunston and Blisworth were becoming bottlenecks and steam tugs were provided to tow strings of waiting boats through.
Under the encouragement of major carriers Fellows Morton & Clayton
Fellows Morton & Clayton Ltd was, for much of the early 20th century, the largest and best-known canal transportation company in England. The company was in existence from 1889 to 1947.
Origins
The company started in 1837 when James Fellows, a ...
, the Grand Junction bought the (old) Grand Union Canal
The Grand Union Canal in England is part of the British canal system. It is the principal navigable waterway between London and the Midlands. Starting in London, one arm runs to Leicester and another ends in Birmingham, with the latter st ...
and the Leicestershire and Northamptonshire Union Canal
The Leicestershire and Northamptonshire Union Canal is a canal in England that is now part of the Grand Union Canal.
It was authorised by an Act of Parliament in 1793 to connect Leicester to the Nene near Northampton and to join the projected li ...
in 1894 and worked with other navigations to encourage more through traffic to London: the Grand Junction was concerned that through traffic was being deterred by the poor condition and high tolls of the railway-owned Cromford Canal
The Cromford Canal ran from Cromford to the Erewash Canal in Derbyshire, England with a branch to Pinxton. Built by William Jessop with the assistance of Benjamin Outram, its alignment included four tunnels and 14 locks.
From Cromford it ran ...
and Nottingham Canal
The Nottingham Canal is a canal in the English counties of Nottinghamshire and Derbyshire. As built, it comprised a long main line between the River Trent just downstream of Trent Bridge in Nottingham and Langley Mill in Derbyshire. At the sam ...
.
 An inclined plane was opened at
An inclined plane was opened at Foxton Locks
Foxton Locks () are ten canal locks consisting of two "staircases" each of five locks, located on the Leicester line of the Grand Union Canal about west of the Leicestershire town of Market Harborough. They are named after the nearby village ...
in 1900, as part of a plan to enable wide barges to use the Grand Union Canal and thus bring more traffic on to the main line of the Grand Junction from the east Midlands. Widening of the locks at Watford
Watford () is a town and borough in Hertfordshire, England, 15 miles northwest of Central London, on the River Colne.
Initially a small market town, the Grand Junction Canal encouraged the construction of paper-making mills, print works, a ...
was also planned, but not carried through. Consideration was given to constructing other inclined planes as part of a plan to enlarge the canals to carry 80-ton barges, but no more were built.
With ever more traffic going by rail, the canal's only significant weapon was low tolls. While this slowed the decline in volumes, it did so only by large reductions in income, and consideration was given to amalgamations with other canals.
Concerns began to develop about the state of repair of the canal via Warwick to Birmingham, on which the Grand Junction was reliant for a through route. In 1925, discussions began with the three Warwick canals and the Regent's Canal, and in 1926 a merger was agreed. The Regent's Canal bought the Grand Junction Canal and the three Warwick canals, and from 1 January 1929 they became part of the (new) Grand Union Canal
The Grand Union Canal in England is part of the British canal system. It is the principal navigable waterway between London and the Midlands. Starting in London, one arm runs to Leicester and another ends in Birmingham, with the latter st ...
.
See also
*Canals of Great Britain
The canals of the United Kingdom are a major part of the network of inland waterways in the United Kingdom. They have a varied history, from use for irrigation and transport, through becoming the focus of the Industrial Revolution, to today's ro ...
* History of the British canal system
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
References
Further reading
* Hadfield, C., and Skempton, A.W., (1979) ''William Jessop, Engineer'' David and Charles Publishers. * Faulkner, Alan H., (1972) ''The Grand Junction Canal'' David and Charles Publishers. * Hassell, John (1819) ''Tour of the Grand Junction, illustrated in a series of engravings, with an historical and topographical description of those parts of the counties of Middlesex, Hertfordshire, Buckinghamshire, Bedfordshire, and Northamptonshire, through which the canal passes'' Published by J. HassellInternet Archive
*''The Mechanics' Magazine, Museum, Register, Journal and Gazette''. (1834) Letter: "Improvement in the Locks of the Grand Junction Canal Company"
Google Books
*Hiscock, Fabian, (2019) ''
External links
* * * {{Coord, 51, 52, N, 0, 39, W, region:GB_scale:1000000, display=title Canals in England Canals opened in 1800